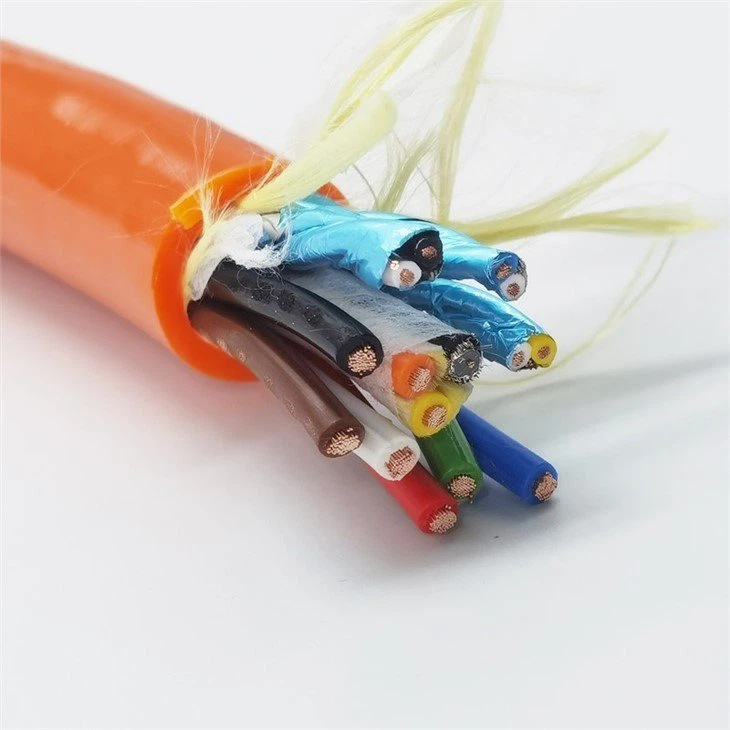
Buoyancy cable and ordinary cable have distinct characteristics and applications:
- Buoyancy Cable: It also known as a buoyant cable or floating cable, is specifically designed to float in water or other fluids. It is engineered with materials that have lower density than the fluid it is submerged in, allowing it to stay afloat. The buoyancy is achieved by incorporating air-filled or lightweight materials, such as foam or hollow sections, into the cables structure.
Buoyancy cables are often used in marine applications, such as underwater telecommunications, offshore oil and gas operations, submarine power transmission, and oceanographic data collection. By keeping the cable buoyant, it helps to minimize dragging and tension on the cable, ensuring stability and enabling proper functioning.
2. Ordinary Cable: An ordinary cable, also referred to as a standard or non-buoyant cable, is designed for general-purpose use and does not incorporate any specific buoyancy features. These cables are commonly used for electrical wiring, data transmission, telecommunications networks, and various industrial and residential applications.
Ordinary cables do not possess the inherent floatation properties of buoyancy cables. Therefore, they are typically used in terrestrial environments where buoyancy is not a requirement. These cables are often made with solid conductors or fiber optic strands surrounded by insulating materials or protective jackets, providing electrical continuity and shielding.
честные казино с быстрыми выплатами
бездепозитные бонусы казино
играть в лучшем казино на деньги
база казино с бездепозитным бонусом
онлайн казино России
casino oyunu
In summary, the key difference between a buoyancy cable and an ordinary cable lies in their design and intended usage. Buoyancy cables are engineered to remain buoyant in fluid environments, while ordinary cables are designed for general-purpose use in terrestrial applications.https://www.bofan-cable.com/product/2-power-2-signal-floating-cable/